Understanding Japan’s Earthquake and Tsunami Risk

Japan is situated in one of the most seismically active regions on Earth, making it highly vulnerable to earthquakes and tsunamis. The country’s unique geological setting, characterized by the convergence of multiple tectonic plates, plays a crucial role in its susceptibility to these natural disasters.
Geological Factors Contributing to Japan’s Vulnerability, Japan earthquake tsunami warning
The Japanese archipelago is located at the meeting point of four major tectonic plates: the Pacific Plate, the Philippine Sea Plate, the Eurasian Plate, and the North American Plate. These plates are constantly moving and interacting, leading to significant seismic activity. The Pacific Plate, for example, is subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate, causing the latter to buckle and uplift, forming the Japanese mountain ranges. This process also generates intense pressure and heat, leading to the formation of volcanoes and the release of energy in the form of earthquakes.
History of Major Earthquakes and Tsunamis in Japan
Japan has a long and tragic history of earthquakes and tsunamis. Some of the most devastating events include:
- The 1703 Genroku earthquake, which struck the Tokai region, causing widespread damage and a large tsunami.
- The 1923 Great Kanto earthquake, which devastated Tokyo and Yokohama, resulting in a massive fire that claimed thousands of lives.
- The 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami, one of the most powerful earthquakes ever recorded, triggered a devastating tsunami that caused widespread destruction and loss of life along the northeastern coast of Japan.
The 2011 Tohoku earthquake, with a magnitude of 9.0, was the most powerful earthquake to hit Japan in recorded history. It triggered a massive tsunami that reached heights of up to 40 meters in some areas, causing extensive damage to coastal communities and infrastructure. The event highlighted the immense destructive power of earthquakes and tsunamis and underscored the importance of preparedness and mitigation measures.
The Pacific Ring of Fire and Japan’s Seismic Activity
Japan lies within the Pacific Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped zone of intense seismic and volcanic activity that encircles the Pacific Ocean. This region is characterized by the convergence of multiple tectonic plates, resulting in frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The Pacific Ring of Fire is home to over 75% of the world’s active volcanoes and is responsible for approximately 90% of the world’s earthquakes.
Characteristics of Japan’s Tectonic Plates and Their Interactions
The specific characteristics of Japan’s tectonic plates and their interactions contribute significantly to the country’s seismic activity. The Pacific Plate is denser than the Eurasian Plate, causing it to subduct beneath the latter. This subduction process generates immense pressure and heat, leading to the release of energy in the form of earthquakes. The rate of convergence between these plates is estimated to be around 8 centimeters per year, which explains the high frequency of earthquakes in Japan.
Japan’s Tsunami Warning System and Response: Japan Earthquake Tsunami Warning
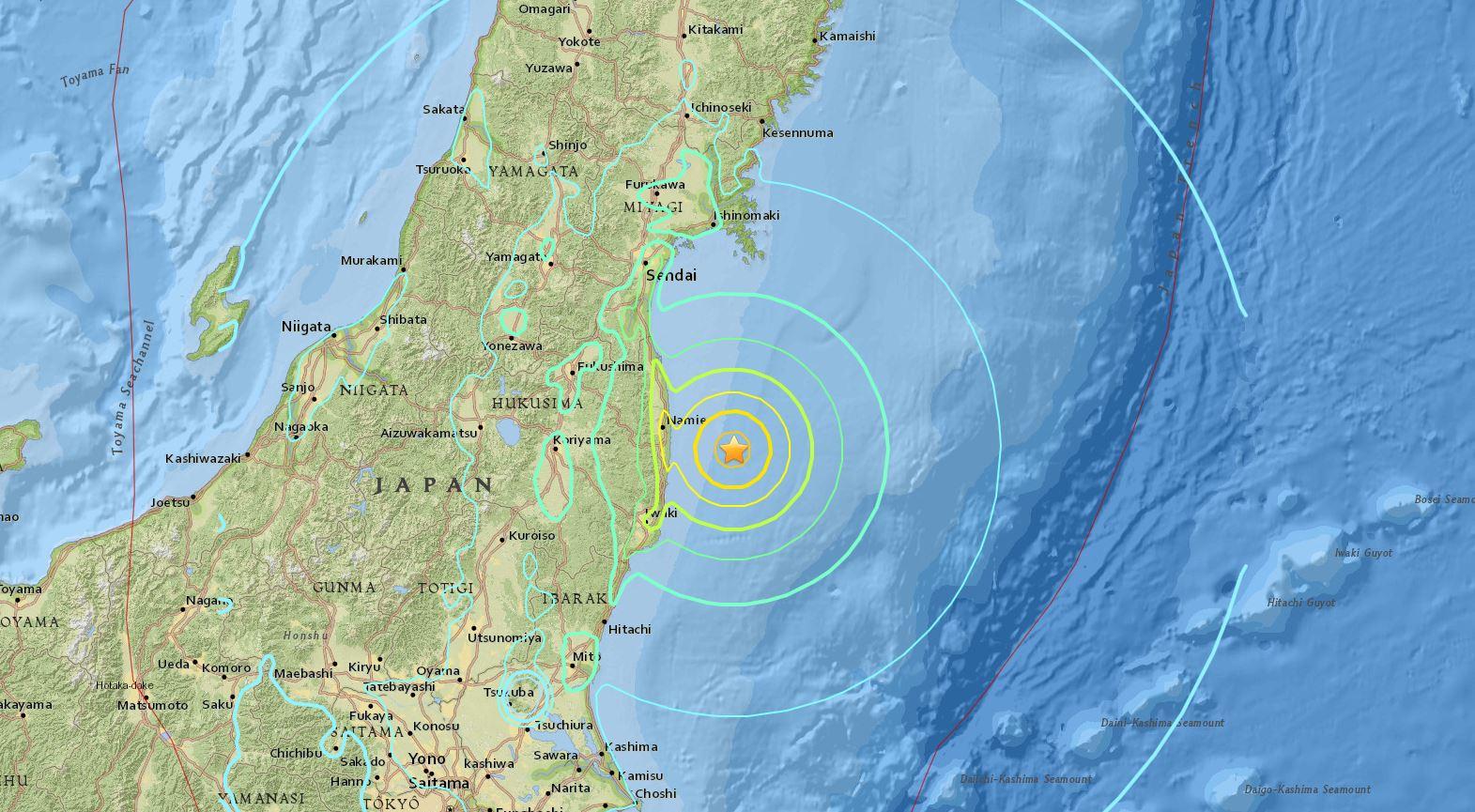
Japan’s Tsunami Warning System is a comprehensive network designed to detect and alert the population about potential tsunamis. It plays a crucial role in minimizing the impact of these natural disasters, which are a recurring threat in the country.
Components and Operation of the Tsunami Warning System
The system relies on a network of sensors, including seismographs and tide gauges, to detect earthquakes and monitor sea level changes. When an earthquake of a certain magnitude occurs, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) immediately analyzes the data to assess the tsunami risk. If a tsunami is predicted, the JMA issues warnings and advisories to the public and relevant authorities.
Role of the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
The JMA is responsible for issuing tsunami warnings and advisories in Japan. The agency utilizes sophisticated computer models to predict the potential size, arrival time, and impact of a tsunami. Based on this analysis, the JMA issues warnings at different levels, ranging from advisories to evacuation orders.
Tsunami Warning Levels and Corresponding Actions
The JMA employs a three-tier warning system to inform the public about the severity of the tsunami threat:
- Tsunami Advisory: This is the lowest level of warning, indicating a small tsunami is possible. The JMA advises people to stay away from coastal areas and monitor updates.
- Tsunami Warning: This warning indicates a significant tsunami is expected. The JMA advises people to evacuate to higher ground immediately.
- Tsunami Emergency Warning: This is the highest level of warning, indicating a large and destructive tsunami is imminent. The JMA urges people to seek immediate shelter in designated evacuation zones.
Effectiveness of the Warning System
Japan’s Tsunami Warning System has proven effective in mitigating damage and saving lives. During the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami, the system provided crucial early warnings, allowing many people to evacuate to safety. However, the 2011 event also highlighted the need for continuous improvement and refinement of the system.
The system’s success is attributed to its rapid and accurate detection of earthquakes and tsunamis, effective communication channels, and well-established evacuation procedures.
Japan earthquake tsunami warning – Japan’s earthquake and tsunami warnings are a serious matter, but even in the face of danger, we can find humor. A good couch joke can lighten the mood, reminding us that laughter is a powerful tool for coping with stress.
Of course, we should always prioritize safety and heed the warnings issued by authorities during these events.
It’s crazy how a natural disaster like the Japan earthquake and tsunami can make you think about the weirdest things. Like, what if all the coffee shops closed down? It’s not like we’d all be scrambling for a cup of joe in a crisis, but it’s funny to think about.
Maybe that’s why there’s a whole Dunkin’ Donuts boycott rumble going on. Anyway, it’s important to remember that even in the face of tragedy, we need to stay calm and prepared. We never know when the next big event will hit, and it’s always best to be ready.